1 Introduction
As a new type of green lighting source, LED has the advantages of energy saving, high efficiency, low carbon, small size, fast response and strong shock resistance. It can provide users with a new lighting experience that is environmentally friendly, stable, efficient and safe and has gradually Develop into a mature semiconductor lighting industry.
In recent years, all countries in the world have started to ban incandescent bulbs, LED will usher in a golden period of growth. In addition, in recent years, LED applications in the TV backlighting, mobile phones, and tablet PCs also ushered in the explosive growth, LED has broad application prospects.
2, Flip LED technology development and status quo
Flip-chip technology is still a relatively new technology concept in the field of LED, but it has been widely used and more mature in the traditional IC industry such as various ball grid array package (BGA), chip size package (CSP), wafer level chip The technologies such as the size package (WLCSP), all using flip-chip technology, have the advantages of high production efficiency, low device cost, and high reliability.
Flip chip technology used in LED devices, the main difference from the IC is that in the LED chip manufacturing and packaging process, in addition to dealing with stable and reliable electrical connections, but also need to deal with the issue of light, including how to make more light Come out, improve the light efficiency, as well as the distribution of light space.
In view of the problems of poor heat dissipation, uneven current distribution of transparent electrodes, surface electrode pads and leads, and the reliability problems caused by gold wires, a conventional 1W LED package has been manufactured. In 1998, JJWierer et al. Power AlGaInN-LED blue chips, they flip-chip the metallized bump AIGalnN chip onto a silicon carrier with an ESD protection diode.
Figure 1 is a picture of their preparation and LED chip schematic cross-sectional view. Their test results show that in the same chip area, flip-chip LED (FCLED) has more light-emitting area than the dress chip and very good electrical characteristics, in the current range of 200-1000mA, the forward voltage (VF) Is relatively low, resulting in higher power conversion efficiency.
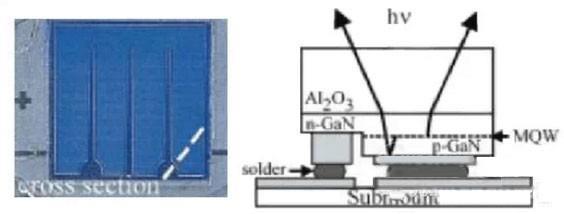
Figure 1 flip-chip LED chip structure and cross-sectional schematic diagram
In 2006, O.B.Shchekin et al. Reported a new multi-quantum well (TFFC-LED) flip-chip LED. The so-called film flip LED, is the thin-film LED and flip the concept of LED combined.
After the LED is flip-chip mounted on the substrate, the laser lift-off technique is used to peel off the sapphire substrate, and then the surface is roughened by photolithography on the exposed N-type GaN layer.
As shown in Figure 2, this thin film LED structure can effectively increase the light efficiency. However, relatively speaking, this structure is more complicated and the cost will be relatively high.
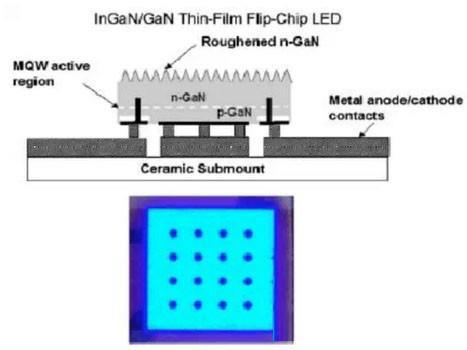
Figure 2 film flip LED chip structure diagram
As silicon-based flip-chips are marketed, it is found that such flip-chip LED chips are at a significant cost disadvantage when competing with flip-chip packaging.
Due to the early stage of LED development, all package supports and forms are designed according to their regular or vertical structure LED chips. Therefore, flip-chip LED chips have to be flip-chip mounted on a silicon substrate, and then the chip is fixed on a traditional bracket The gold electrode is used to connect the electrode on the silicon substrate with the electrode on the holder.
Making the existence of gold-plated package within the device there is no advantage of the use of flip-gold-free package; but also increased the cost of the substrate, making the price higher, did not play the advantages of flip-chip LED.
To this end, as early as 2007, the company introduced a ceramic-based flip-LED package products. This type of product, ceramic both as a flip-chip support substrate, but also as a whole package bracket, to achieve the entire package light source miniaturization.
This package is to first flip-chip bonding (Bonding) on the ceramic substrate, and then the phosphor coating, and finally mold (Molding) method of making a lens, this method will LED chips and packaging technology combined , Reducing costs.
This structure completely eliminates the gold wire and significantly improves the heat dissipation. The typical thermal resistance is <10 ° C / W, significantly lower than the traditional K2 package (typically 10-20 ° C / W).
With the further application and development of flip chip technology, a Direct Attach (DA) flip chip appeared in 2012. In the following years, various companies started to research and develop this type of flip chip.
The chip in the structural change is that the LED chip surface P, N two metal pad geometry to enlarge, while ensuring that the spacing between the two pad enough, so that the flip-chip LED chip can be ceramic substrate Even on the PCB board directly on the chip, so 40mil flip chip pad size to reach the SMT chip placement accuracy requirements, simplifying the flip chip welding process, reducing the overall cost.
So far (mid 2014) Flipped DA chips have basically matured, the market sales increased gradually, the future will become the mainstream of high-power LED chips.
Based on the direct mount DA chip, the white chip (some companies called the no-package or no-package) products began to develop in 2013, as shown in FIG. 6. It is in the process of manufacturing flip-chip DA completed at the same time the phosphor coating, the application can be directly on the PCB chip, can be used directly as a package light source.
The advantage is the small size of LED devices, chip direct chip can reduce the thermal interface, further reducing the thermal resistance, thermal performance and further improve. So far, the white chip is still in the research and development stage, the application of the market is not yet mature, we need to work together to promote the development of white light chip technology and applications.

Figure 3 white chip and package diagram
3, flip LED chip production process
Flip LED chip production process, as shown in Figure 4, the overall can be divided into LED chip production and substrate manufacturing two lines, chip and substrate manufacturing is completed, the LED chip flip-chip mounted on the substrate surface, the formation of inverted With LED chips.
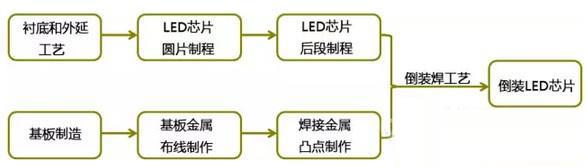
Figure 4 flip-chip LED chip flow chart
3.1, sapphire substrate and GaN epitaxial process technology
For a flip chip, the light is on the sapphire side, so making a patterned substrate (PSS) prior to epitaxy will favor the blue light and reduce light reflection at the GaN and sapphire interfaces. Therefore PSS graphics size size, shape and depth of light output efficiency has a direct impact. In the actual development and production of the need for flip-chip features, the optimization of the substrate graphics, the highest light efficiency.
In the case of GaN epitaxy, the light absorption of the layers is different from that of the packaged chips due to the light emitting of the flip chip on the sapphire side. Therefore, it is necessary to use the epitaxial buffer, the N-GaN layer, the multi-layer quantum well (MQW) And P-type GaN layer thickness and doping concentration adjusted to fit the light-emitting requirements of the flip-chip to improve the light efficiency, while suitable for flip-chip manufacturing process ohmic contact needs.
3.2, flip LED wafer process
The process of flip chip fabrication is roughly the same as the wafer fabrication of the finished chip, requiring etching on the epitaxial layer to expose the underlying N-type GaN; then ohmic contact electrodes are fabricated on the P and N electrodes, respectively, and then fabricated on the chip surface Passivation protective layer, the final production of metal pads for welding, the production process shown in Figure 5.
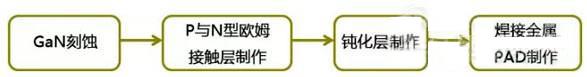
Figure 5 flip LED wafer production process
Flip chips need to be made with the electrode facing downwards compared to the case of the flip chip. This special structure makes the flip chip have some special requirements in some process steps. For example, the ohmic contact layer must have high reflectivity, so that the light directed to the surface of the chip electrode can be reflected back to the sapphire side as much as possible to ensure Good light output efficiency.
Flip-chip layout also needs to be based on the current uniform distribution, to do the most optimal design. As the wafer production process, GaN etching (Mesa etching), N-type contact layer production, passivation layer production, PAD production of solder metal are basically the same as the chip, here is not described in detail, the following focus on flip Chip special process for a brief description.
In the LED chip production process, the ohmic contact layer process is the core of chip production, especially important for flip chip. The ohmic contact layer not only has the traditional function of electrically connecting, but also functions as a reflective layer, as shown in FIG. 9.
In the P-type ohmic contact layer production process, to select the appropriate ohmic contact material, it is necessary to ensure that the P-type GaN contact resistance is small, but also to ensure ultra-high reflectivity. In addition, the metal layer thickness and annealing process on the ohmic contact characteristics and reflectance is very large, this process is crucial, which is related to the entire LED light efficiency, voltage and other important technical parameters, is the most important flip-chip LED technology Part of the ring.
Currently, the ohmic contact layer is generally made of silver (Ag) or silver alloy material. Under appropriate process conditions, a stable high-performance ohmic contact can be obtained while ensuring that the reflectivity of the ohmic contact layer exceeds 95 %.
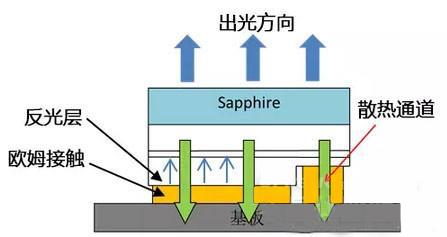
Figure 6 flip chip light direction, cooling channels, ohmic contact, reflective layer position diagram
3.3, Flip LED chip after the process
As with the LED chips are installed, after the wafer process, but also includes the chip after the process, the process shown in Figure 7, including grinding, polishing, cutting, splitting, testing and classification and other processes. Here the process, the only difference is the test process, the other processes are basically the same as the chip is loaded, not repeat them here.
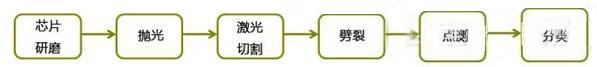
Figure 7 LED chip back-end process flow chart
Flip chip due to the light in the electrode surface and the electrode in different directions, so after cutting the chip point measurement, the probe pin in the LED front electrode measurement, the LED light is emitted from the back. To test the LED's optical characteristics (wavelength, brightness, half-wave width, etc.), the light must be received from below the probe station.
Therefore, flip-chip point measuring machine is different from the spot-measuring machine, the light-metering device (probe or integrating sphere) must be placed under the probe and the chip, and the chip's stage must be transparent to light Characteristics of the test.
Therefore, the flip chip point measuring machine needs special manufacturing or modification.
Related News
- LED High Bay Light Brief Introduction
- Vietnam LED lighting market has become the emerging focus?
- LED Outdoor Lighting
- Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge
- LED lamp bead welding process dead lamp reason
- Why there is no street light on the highway? - Dec 29, 2017 -
- LED packaging process, how to do a good job of anti-sulfur measures
- High-power LED lamp beads characteristics and technical parameters
- RGB LED three white LED forming principle
- Improve the light extraction efficiency of thermal resistance power LED pack
- LED packaging Collection: I do not know the LED packaging process knowledge
- LED driver power potting use
- Experimental Study on Improving the Temperature Resistance of LED Light Source
- LED Floodlight structure
- Advantages of Driverless Floodlights
- LED flood light installation instructions
- Advantages Of LED Floodlight
- LED flood light applications
- LED six technology to lead the future
- Small out of the high light flux density under the trend of LED package substrate








 Jackson
Jackson
 sales01@newlamp-lighting.com
sales01@newlamp-lighting.com





